Endemic species of Talamanca

The Talamanca Mountain Range, located in Costa Rica, is home to numerous species unique in the world. Among them are the Talamanca red-eyed frog (Isthmohyla rivularis) and the Talamanca salamander (Bolitoglossa diminuta), two emblematic amphibians that illustrate the importance of protecting this ecosystem.
Endemic species of Talamanca
Amira’s bell frog (Diasporus amirae)
Description
Diasporus amirae, known as “Amira’s bell frog,” is a species recently discovered in the Talamanca mountain range, Costa Rica. It lives mainly on the Plátano hill, at altitudes of about 1,000 meters above sea level. This small frog, which measures between 0.5 and 2 centimeters, is distinguished by its dark brown color and bluish-gray belly. It is also more robust compared to other species of its genus.
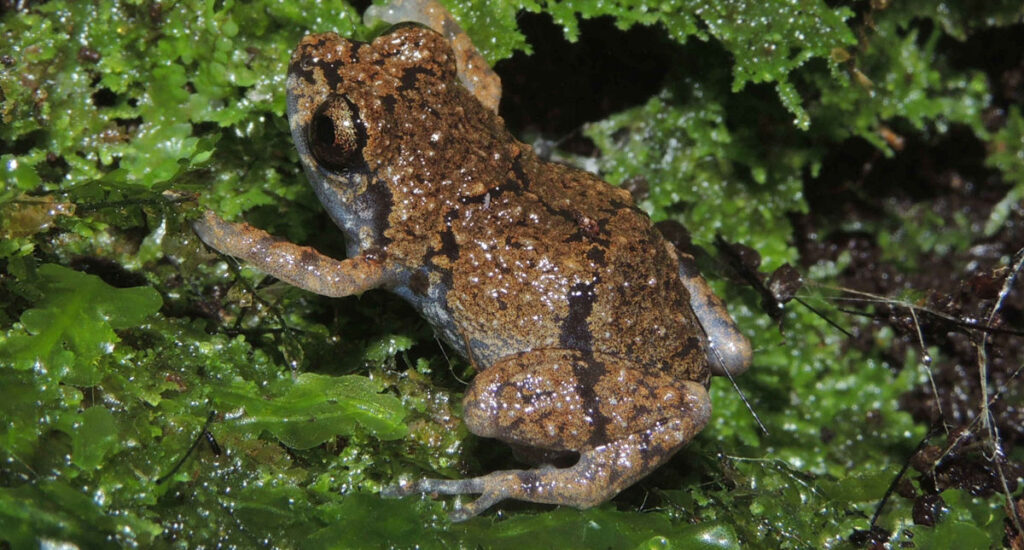
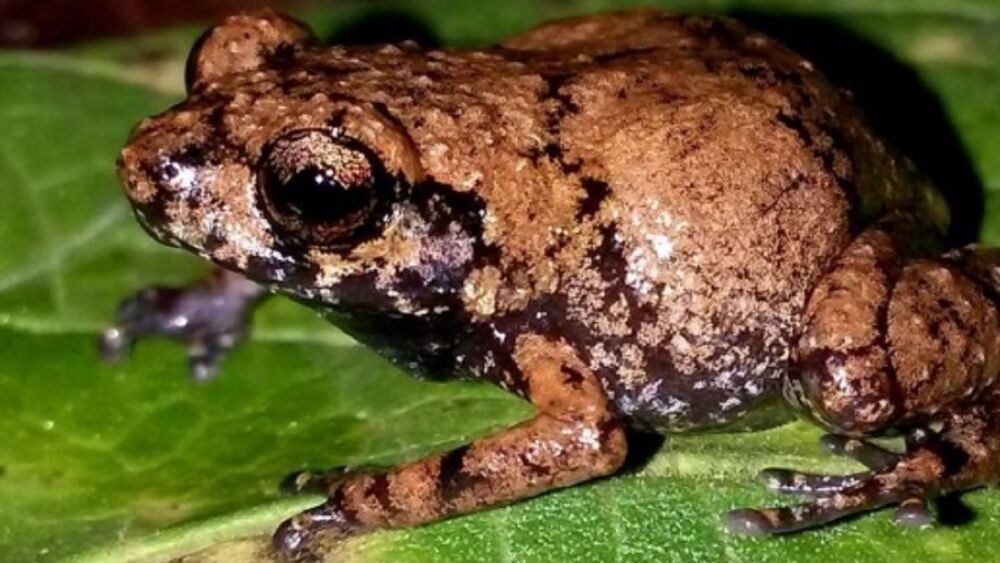


Habitat and Behavior
Its behavior is peculiar, since it lives both close to the ground, in holes, and in the canopy of trees at heights of 8-9 meters, which contrasts with the typical habit of its genus to stay at lower altitudes. Its song, similar to the sound of a bell, is infrequent, which makes it difficult to locate.
Conservation
Although it is not currently listed as an endangered species, it faces challenges due to the high rainfall in the region, which complicates research and monitoring. So far, only ten male individuals have been recorded, suggesting that the species may have a limited distribution and require special protection to ensure its survival.
Talamanca Salamander (Bolitoglossa diminuta)
Characteristics
The Talamanca salamander is a tiny and unique amphibian. It is a member of the genus Bolitoglossa, known for its adaptation to arboreal environments and its ability to breathe through its skin.
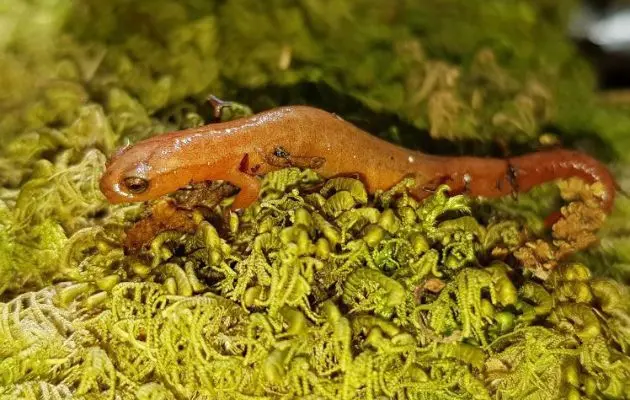
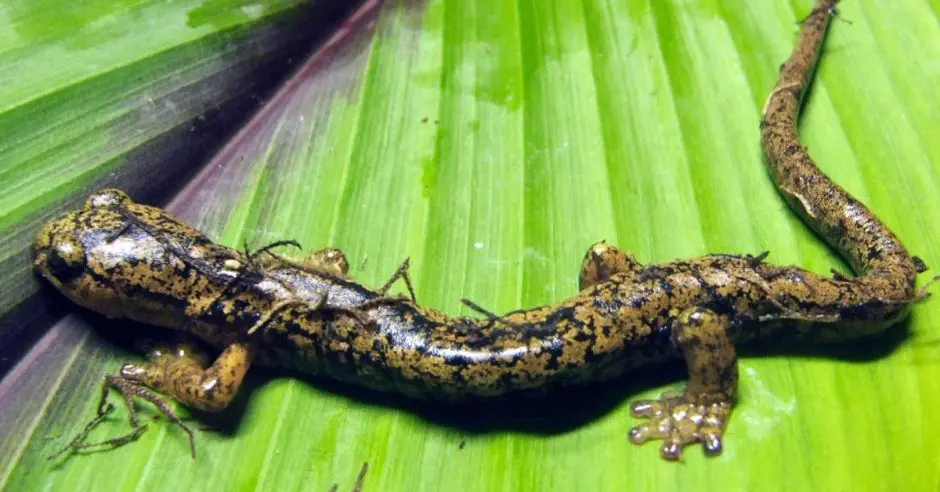



- Size: Adult males measure only 27 mm from the mouth to the base of the tail, making it one of the smallest species of its genus.
- Habitat: It lives mainly in the canopy of cloud forests, frequenting bromeliads and other plants that provide shelter and constant humidity.
Ecological Importance
The discovery and study of Bolitoglossa diminuta highlights the extraordinary biodiversity of Costa Rica. This country has one of the highest diversities of salamanders in the world, and the existence of this species highlights the importance of continuing to research and protect the mountain ecosystems that are their home.
Conclusion
The endemic species of Talamanca, such as the Amira bell frog and the Talamanca salamander, represent an invaluable natural heritage. Protecting their habitats is essential to preserve not only these unique species, but also the ecological richness of the region. Conservation of the Talamanca cloud forests not only benefits these amphibians, but also ensures the balance of a vital ecosystem for Costa Rica and the world.
Sensorial Sunsets
Endemic species of Talamanca
Navigate articles